Selection Sort
Select-sort is a simple and intuitive sorting algorithm. It works by first finding the smallest (large) element in the unsorted sequence and storing it at the beginning of the sorted sequence, then continuing to find the smallest (large) element from the remaining unsorted elements and placing it at the end of the sorted sequence. And so on until all the elements are sorted.
Algorithm description
Ordering results can be obtained by direct selection sorting of n records through n-1 direct selection sorting. The specific algorithm is described as follows:
- Initial state: disordered region is R[1..n], ordered region is empty;
- i sort (i=1,2,3... n-1) At the beginning, the current ordered and disordered regions are R[1..i-1] and R(i.. n). The run sort selects the record R[k] with the smallest keyword from the current unordered area and swaps it with the first record R in the unordered area, so that R[1..i] and R[i+1..n) become a new ordered area with 1 more records and a new unordered area with 1 less records, respectively.
- n-1 is done. The array is ordered.
GIF presentation
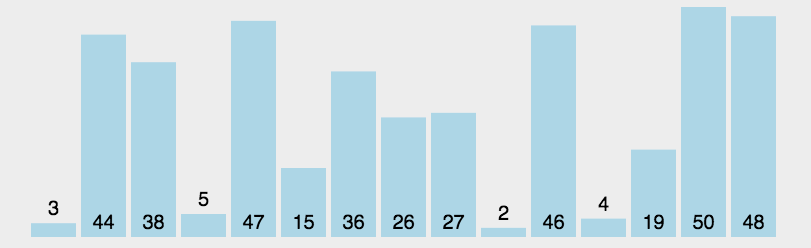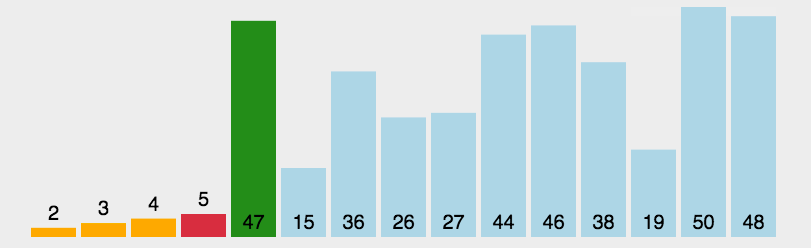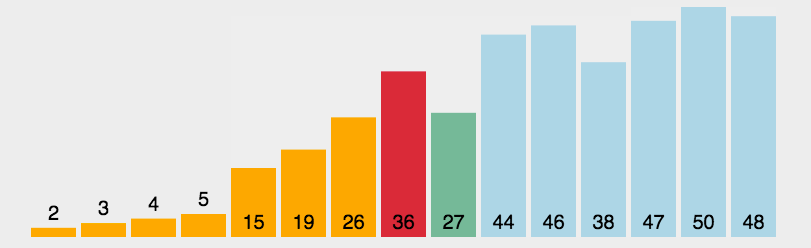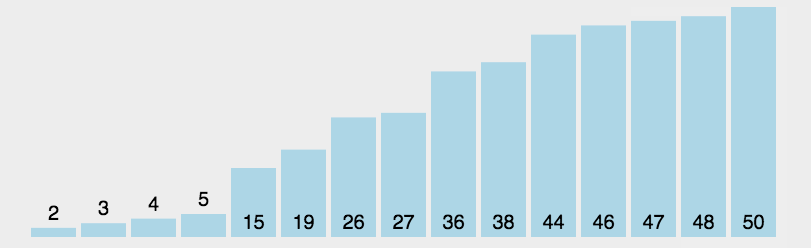
Code demo
const select = (list: number[]): number[] => {
const size = list.length;
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
let minIndex = i;
for (let j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {
if (list[minIndex] >= list[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (list[i] !== list[minIndex]) {
list[i] = list[i] ^ list[minIndex];
list[minIndex] = list[i] ^ list[minIndex];
list[i] = list[i] ^ list[minIndex];
}
}
return list;
};Algorithm analysis
One of the most stable sorting algorithms, because whatever data goes in is O(n2) time complexity, so when using it, the smaller the data size, the better. The only benefit may be that it doesn't take up extra memory space. In theory, selection sorting may also be the most common sorting method that people think of.