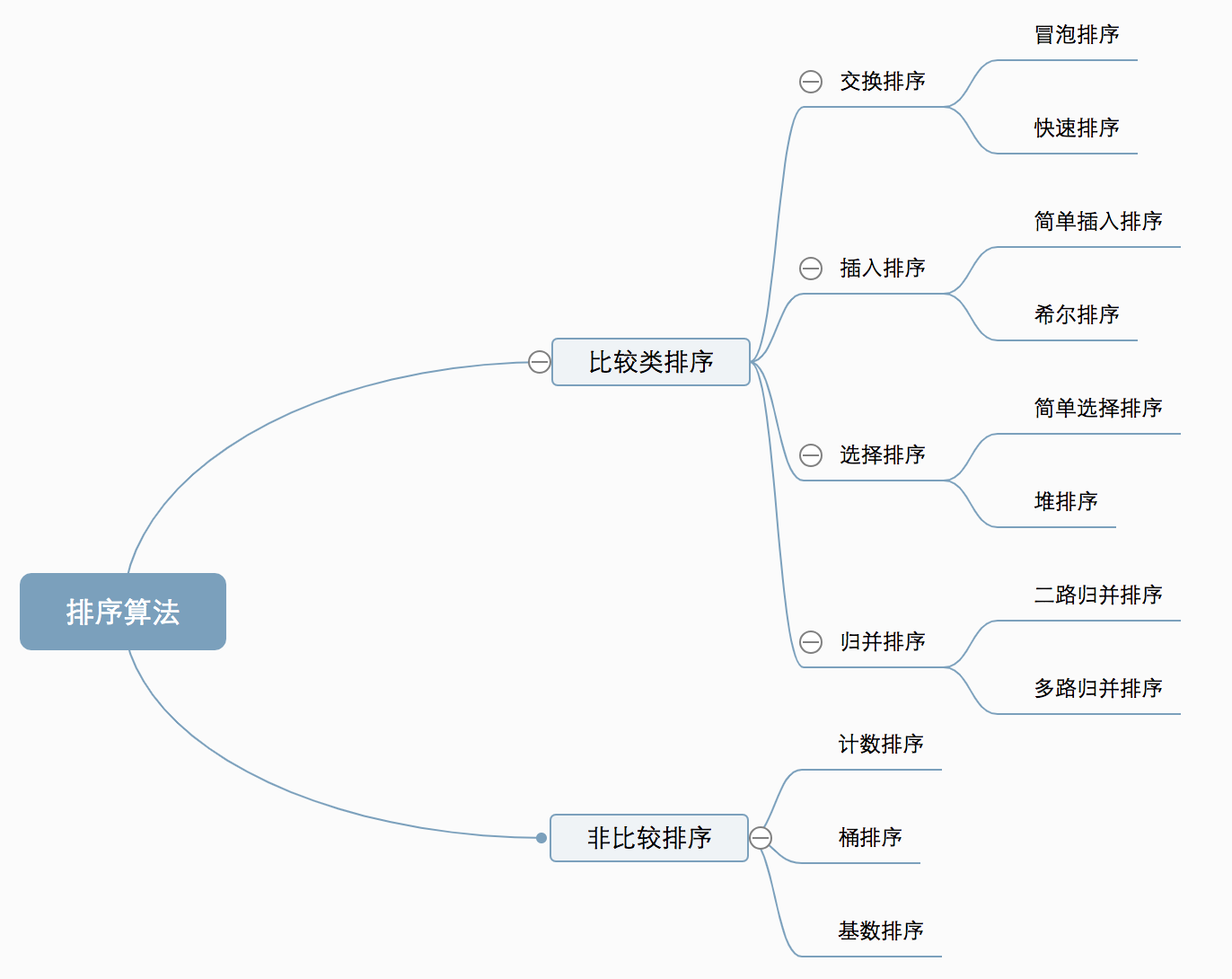
Ten classic sorting algorithms
The ten common sorting algorithms can be divided into two broad categories:
- Comparator sort:By comparison to determine the relative order between elements, because its time complexity can not break through O(nlogn), so it is also called nonlinear time comparison class sorting.
- Non-comparison sort:Instead of determining the relative order between elements by comparison, it can break through the time lower bound based on comparison sort and run in linear time, so it is also called linear time non-comparison sort.
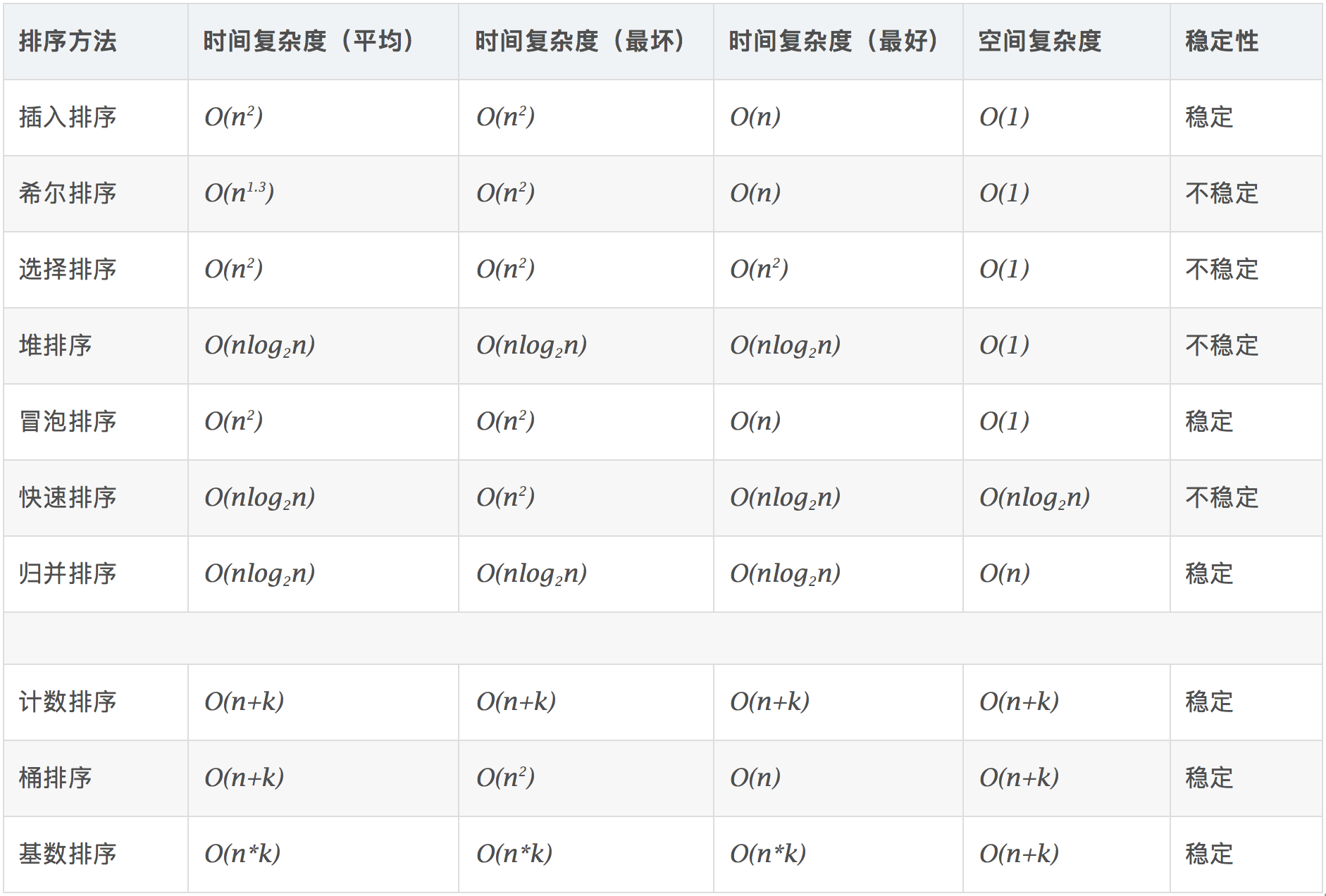
Algorithm complexity
Related concept
- Stable: If a was originally in front of b and a=b, a is still in front of b after sorting.
- Unstable: If a originally comes before b and a=b, a may come after b after sorting.
- Time complexity: The total number of operations on sorted data. Reflects what rule the number of operations presents when n changes.
- Spatial complexity: refers to the measure of the storage space required when the algorithm is executed in the computer, and it is also a function of the data size n.