计数排序( Count Sort )
计数排序(counting sort)就是一种牺牲内存空间来换取低时间复杂度的排序算法,同时它也是一种不基于比较的算法。这里的不基于比较指的是数组元素之间不存在比较大小的排序算法,我们知道,用分治法来解决排序问题最快也只能使算法的时间复杂度接近 Θ(nlogn),即基于比较的时间复杂度存在下界 Ω(nlogn),而不基于比较的排序算法可以突破这一下界。
算法描述
- 找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素;
- 统计数组中每个值为 i 的元素出现的次数,存入数组 C 的第 i 项;
- 对所有的计数累加(从 C 中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加);
- 反向填充目标数组:将每个元素 i 放在新数组的第 C(i)项,每放一个元素就将 C(i)减去 1。
动图演示
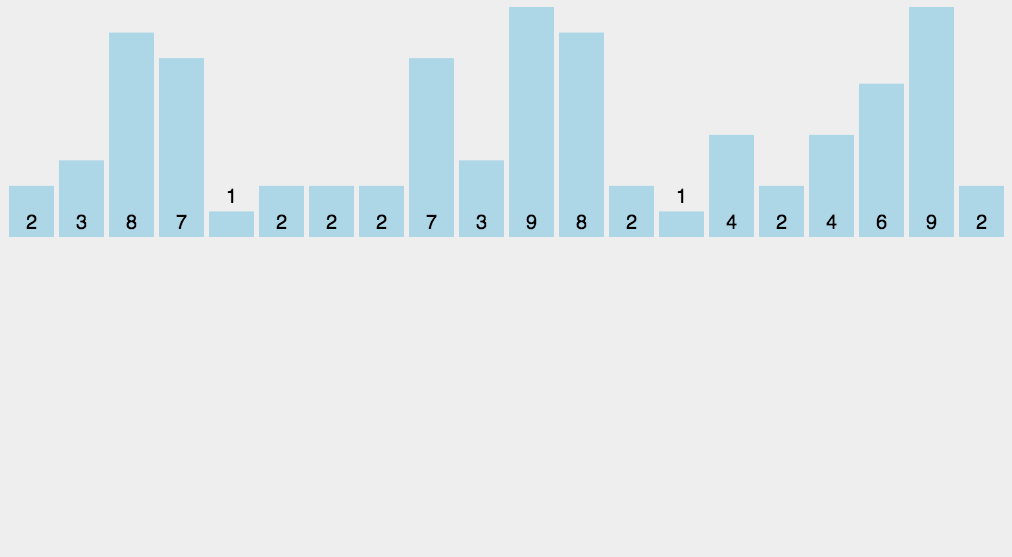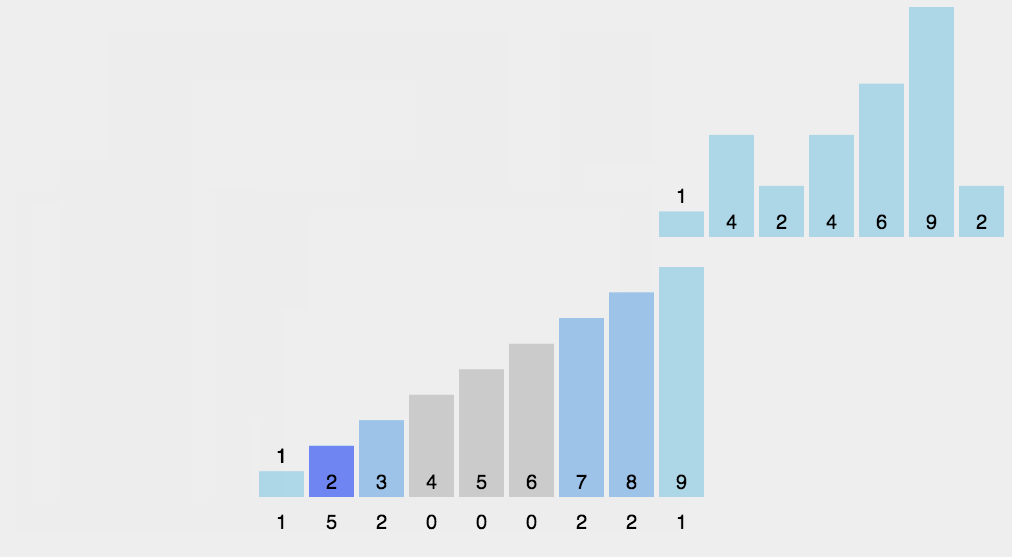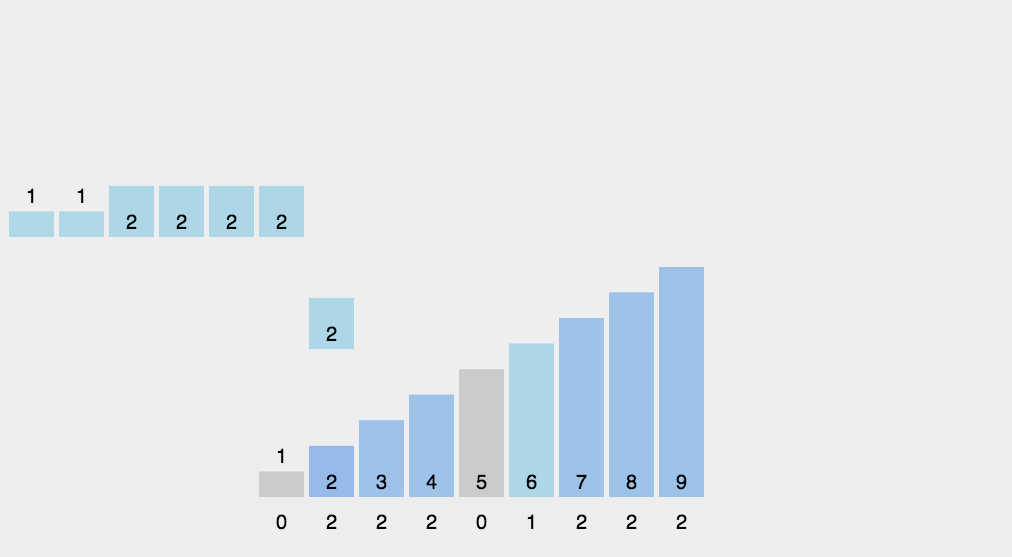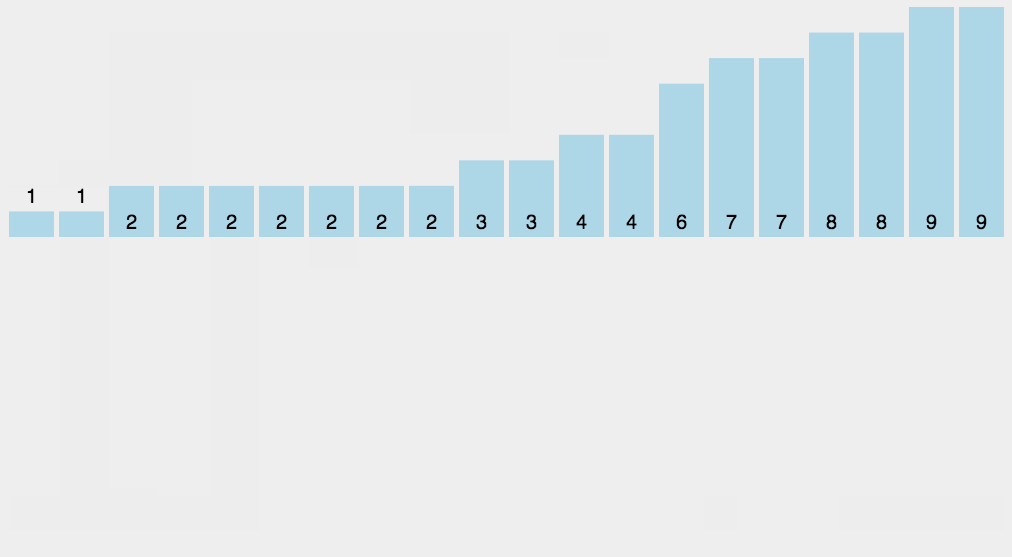
代码演示
ts
const getMax = (list: number[]) => {
let max = list[0];
for (let i = 1; i < list.length; i++) {
if (max < list[i]) {
max = list[i];
}
}
return max;
};
/**
* @description: 计数排序
* @param {Array<number>} list
* @return {Array<number>}
*/
const count = (list: number[]): number[] => {
if (list.length <= 1) return list;
const max = getMax(list);
const countList = new Array(max + 1).fill(0);
list.forEach((item) => {
if (!countList[item]) {
countList[item] = 1;
} else {
countList[item]++;
}
});
const result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < countList.length; i++) {
while (countList[i]) {
result.push(i);
countList[i]--;
}
}
return result;
};算法分析
计数排序是一个稳定的排序算法。当输入的元素是 n 个 0 到 k 之间的整数时,时间复杂度是 O(n+k),空间复杂度也是 O(n+k),其排序速度快于任何比较排序算法。当 k 不是很大并且序列比较集中时,计数排序是一个很有效的排序算法。